Survey Services
Survey monument fixing
Survey monument fixing involves placing permanent markers (monuments) at key points on a piece of land to define boundaries and reference points for future surveys. It involves the establishment of precise reference points (benchmarks) with known elevations above a specific datum, usually sea level. These markers are crucial for ensuring the long-term accuracy and reliability of land surveys.
- Purpose of this Survey is to get reference points (providing fixed points that can be used for future surveys and mapping).
- Methods used
- Link Statics and Triangulation Statics (GNSS)
Link Statics and Triangulation Statics are two key concepts in context of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). Both play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of GNSS-based positioning.
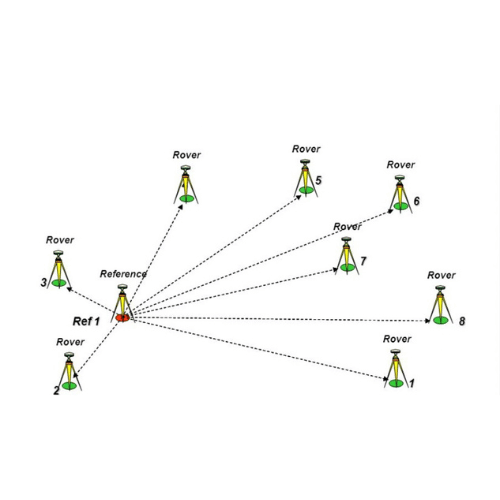
Link Statics refer to the static positioning method used to determine accurate coordinates of a point by observing the position over a long period.
This method typically involves:
- Extended Observation
- Duration : Data is collected from the GNSS Receiver over a prolonged period, From several minutes to hours, to Average out transient errors and improve accuracy.
- Base station and Rover : Involves using a base station with known coordinates and a rover receiver. The base station sends correction data to the rover to enhance positioning accuracy.
- Differential Correction
- Correction Data : The base station calculates the errors in GNSS signals and transmits these corrections to the rover in real-time or post- processed.
- Error Mitigation : The rover applies these corrections to its measurements to correct for various errors, including atmospheric delays and satellite orbit inaccuracies.
- Carrier Phase Measurements
- Precision : Utilizes carrier phase measurements, which are more precise than code phase measurements, to achieve high-accuracy positioning.
- Applications :Surveying Construction and Engineering Environmental Monitoring
Triangulation statics involve determining the position of a point by forming triangles to it from known points. In GNSS, this concept is extended through trilateration, satellite constellation geometry.
This method typically involves:
- Distance Measurement
- Pseudorange Calculation : The GNSS receiver measures the time it takes for signals to travel from multiple satellites. This time is converted into distances (Pseudorange).
- Satellite Geometry : The receiver needs signals from at least four satellites to solve for its three-dimensional position and clock error.
- Geometric Calculation
- Sphere Intersection : The position of the receiver is determined by intersecting spheres centered on each satellite, where the radii of the spheres are the calculated distances.
- Least Squares Adjustment : Often used to adjust the position estimate and account for any measurement errors.
- Applications
- Navigation
- Mapping and surveying
- Scientific Research
Link statics and Triangulation Statics (Trilateration) are often used together to achieve accurate GNSS positioning.
- RTK (GNSS)
Rea-Time Kinematic (RTK) GNSS is a precise positioning technique that uses carrier-based ranging and differential correction to achieve centimetre-level accuracy in real time.
- Key Components
- Base station
- Rover
- Setup and Preparation
- Base Station Setup
- Location: Setup the base station at a known, stable location with a clear view of the sky. This location can be a permanent or temporary benchmark with known coordinates
- Communication: Ensure the base station can transmit correction data to the rover via radio, cellular, or internet connection.
- Rover Setup
- Mounting : Equip the rover with a GNSS receiver and antenna, and mount it on a surveying instrument or vehicle as needed.
- Calibration :Ensure the rover with a GNSS receiver and antenna, and mount it on a surveying instrument or vehicle as needed.
- Traverse Survey Process
- Initial Calibration
- Base station calibration
- Rover Calibration
- Field Survey
- Start point
- Traverse Measurement
- Point Recording
- Data Collection
- Real-Time Data
- Observation Quality
- Post-Processing and Analysis
- Data Review
- Quality Check
- Adjustment
- Data Integration
- Coordinate Transformation
- Mapping and Analysis
- Applications
- Geodetic Surveys
- Construction
- Land Surveys
- Engineering Projects
- Benefits
- High Accuracy
- Efficiency
- Real-Time Feedback
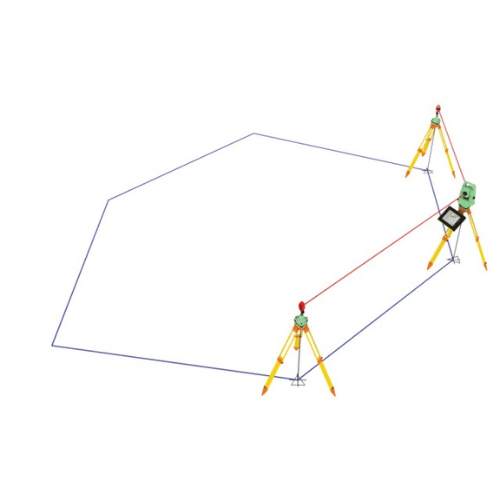
- Closed Traverse (Total Station and Digital Level)
The closed traverse method is a surveying technique used to determine the positions of a series of points in a closed loop, ensuring that the start and end points of the traverse connect to form a closed polygon. This method can be carried out using a digital level and a total station to achieve high accuracy in levelling and angular measurements.
By carefully setting up and calibrating the equipment, executing the traverse, and performing post-processing adjustments, surveyors can ensure reliable and accurate results for various applications.

