Survey Services
Underground Utility survey
An underground Utility survey is a crucial process that involves locating, identifying and mapping subsurface utilities such as pipes, cables and other infrastructure elements. This type of survey is essential for construction, excavation and maintenance projects to avoid damaging existing utility and to ensure safety and compliance.
- Key components
- Utility Detection
- Utility Mapping
- Documentation
- Methods and tools
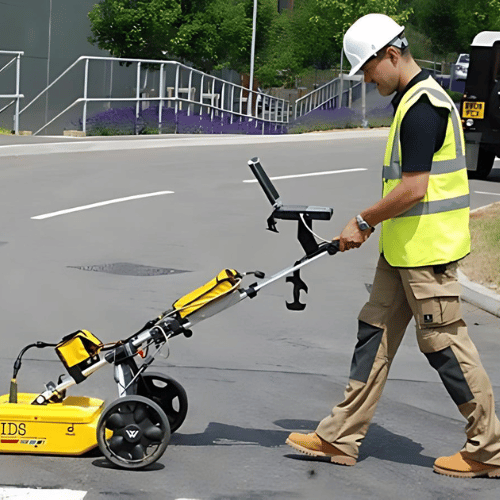
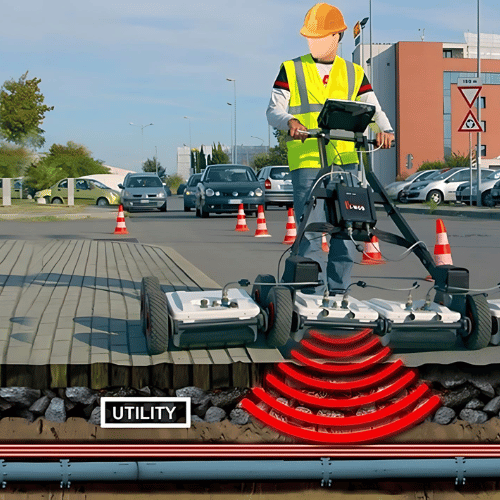
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Description : Uses radar pulses to detect and map Subsurface utilities. It is effective for locating non-metallic utilities such as plastic pipes.
- Advantages : Non-invasive, provides detailed images and can detect a variety of materials
- Limitations : Interpretation can be complex and effectiveness may be reduced in certain soil conditions.


- Electromagnetic Induction (EMI)
- Description : Uses Electromagnetic fields to detect metallic utilities. Commonly used for locating electrical cables, metal pipes and other conductive materials.
- Advantages : Accurate for metallic objects easy to use and widely available.
- Limitations : Ineffective for non-metallic utilities and can be influenced by nearby metal objects.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
- Description : Uses RFID tags attached to utilities to identify and locate them. RFID readers detect these tags and provide location data.
- Advantages : Accurate identification, can be used in various environments and easy to integrate into existing systems.
- Limitations : Requires utilities to be tagged, which may not be feasible for all existing infrastructure.
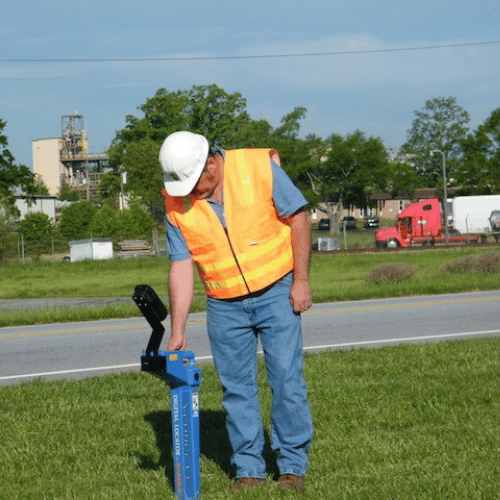
- Acoustic Locators
- Description : Uses sound waves to detect and locate utilities, especially useful for detecting leaks in pipes.
- Advantages : Effective for detecting leaks and can work on various pipe materials.
- Limitations : Requires specialized equipment and may be less effective in noisy environments.
- Hydro Vacuum Excavation (Potholing)
- Description : Uses vacuum technology to excavate small test holes to visually confirm the location and depth of utilities.
- Advantages : Provides accurate location and depth information and minimises damage to utility.
- Limitations : Invasive and time consuming compared to non-invasive methods.
- Applications
- Construction Planning
- Maintenance & Repair
- Infrastructure Development
- Environmental Assessments
- Safety Compliance
- Process
- Planning
- Data Collection
- Data Processing
- Verification
- Reporting
- Benefits
- Safety
- Cost Saving
- Efficiency
- Compliance
- Improved Planning
- Output
The primary output of an underground utility survey is a detailed map showing the location, depth, and type of all detected utilities. These maps can be provided in various formats including
- 2D Utility Map
- 3D Models
- GIS Data
Underground utility surveys are essential for the safe, efficient, and compliant management of construction and infrastructure projects, providing valuable insights into the complex network of subsurface utilities.

